

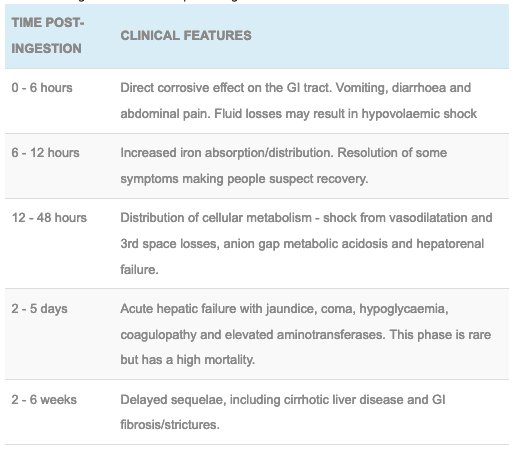
The second stage involves resolution of GI symptoms, with silent absorption of toxic amounts of iron. 17 The first stage of iron poisoning occurs within the first few hours and is characterized by abdominal pain, vomiting, and diarrhea. However, the emergency physician must be aware of overlapping presentations. Traditionally, clinicians have attempted to characterize iron poisoning by clinical stages according to symptoms. The net effect is shock and metabolic acidosis.


Iron disrupts oxidative phosphorylation and promotes the formation of free radicals, contributing to cell death. Systemic effects occur if enough iron is absorbed. Iron is a corrosive with the potential to cause hemorrhage, hypovolemia, and GI perforation. Normally, the TIBC far exceeds the serum iron concentration, resulting in no circulating unbound iron. The total iron-binding capacity (TIBC) represents the amount of iron that transferrin can bind. Iron is transported globally bound to transferrin. The body protects itself by binding iron to ferritin. Exposure to children's chewable vitamins rarely causes severe iron poisoning.įree unbound iron is toxic to tissues. Exposures above 50 mg/kg are potentially fatal. Ingestion of greater than 20 mg/kg will often produce GI upset. Toxicity is dependent on the amount of elemental iron ingested. 1, 2 Iron is readily available in the home, with many preparations resembling chewable candy. There are over 30,000 iron ingestions annually. Iron poisoning is the leading cause of accidental death from pharmaceutical agents in young children. Cantor MD, in Pediatric Emergency Medicine, 2008 Iron Poisoning Tachycardia and acidosis may develop.Deborah J. Stage II- GI sxs resolve, nonspecific malaise.Stage I (w/in 30 mins) – N/V/D, hematemesis or hematochezia.Consider deferoxamine if level > 500 mcg/dL or if CV collapse, otherwise supportive cares.If > 6 hrs Goes by w/o sxs, unlikely to become toxic. Monitor levels and watch for symptoms.Alkalinize the urine to enhance elimination.Sx: Respiratory alkalosis, N/V, tinnitus, lethargy, coma Toxic range: >150 mg/kg (Symptoms more important than level) Stage III (48-72 hrs) – Liver fxn abnormalities peak, N/V/anorexia return.Stage II (> 24 hrs) – Transaminase elevation occurs.Stage I (12-24 hrs) – N/V or asymptomatic.Give 150 mg/kg loading dose over 15 minutes, then 50 mg/kg over 4 hours, followed by 100 mg/kg over remaining 16 hours. N-acetylcysteine (NAC) therapy administered over 20 hours.Plot on Rumack-Matthew nomogram to determine potential for toxicity.Obtain levels and LFTs – do not wait to treat until levels return if concerning amount of drug was ingested.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
